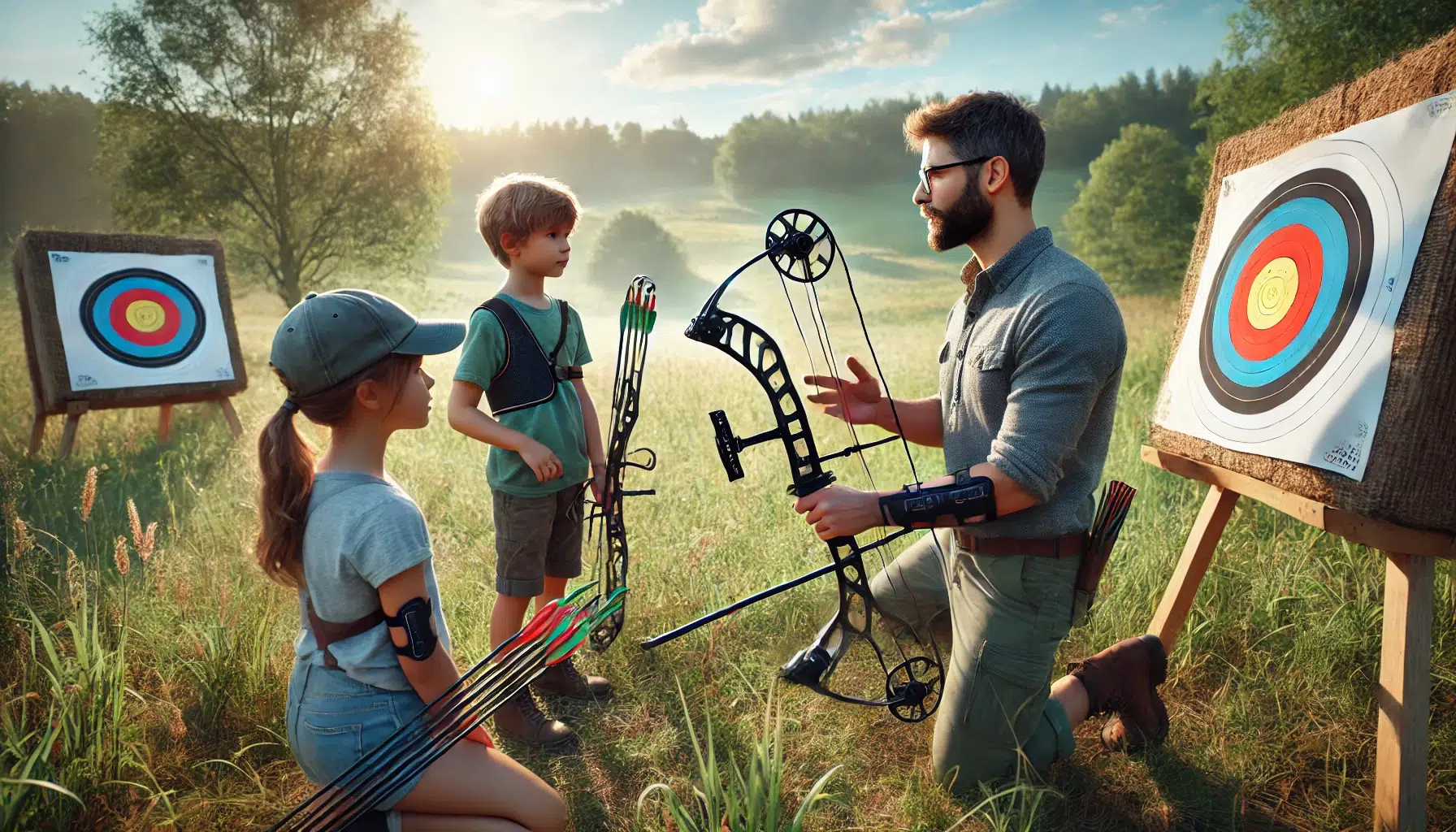

Basic Archery Safety Rules Every Archer Must Follow
Archery is a sport built on precision, discipline, and control. From beginners learning their first stance to professionals competing at

Archery is one of the oldest arts still practiced today, with a history stretching back tens of thousands of years. What began as a vital tool for survival has evolved into a celebrated sport and cultural tradition across the globe.
The earliest evidence of archery dates back to around 20,000–10,000 BCE. Archaeologists have discovered stone arrowheads and bow fragments in Africa and Europe, indicating that prehistoric humans used bows and arrows for hunting.
In ancient times, the bow was not just a weapon—it was a lifeline. It allowed early humans to hunt animals from a distance, improving their chances of survival.
In the Middle Ages, archery reached its peak as a military force:
This period saw major technological and tactical developments in archery, making it a fearsome weapon of war.
With the invention of gunpowder and firearms in the 16th century, archery gradually lost its place in modern warfare. Guns required less training and were more lethal at longer ranges.
However, archery didn’t disappear—it transitioned into a recreational and competitive sport.
Archery remains a symbol of discipline, skill, and tradition. Many indigenous communities still practice it for hunting or ceremonial purposes, and it continues to be a source of pride and cultural identity in places like Bhutan, Korea, and Mongolia.
Conclusion:
From prehistoric hunts to Olympic glory, archery has remained a powerful force throughout human history. It’s a testament to the timeless connection between humans, precision, and the pursuit of mastery.

Archery is a sport built on precision, discipline, and control. From beginners learning their first stance to professionals competing at
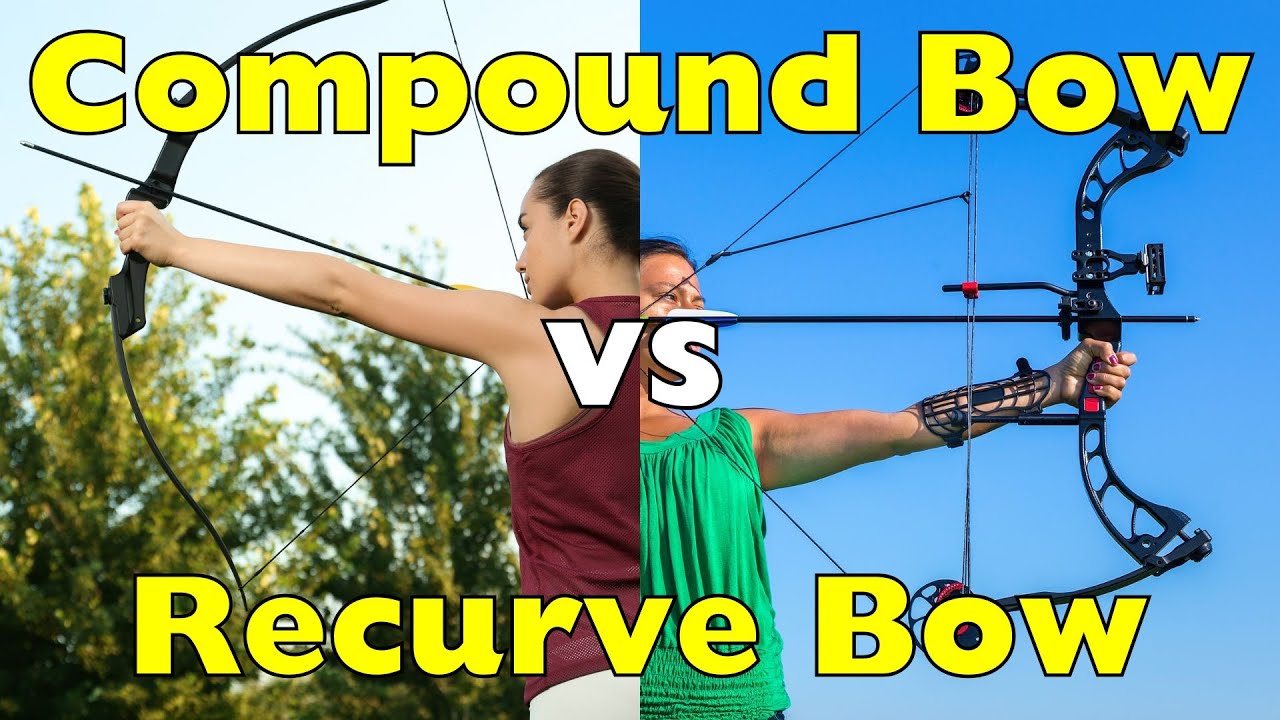
When starting archery, one of the first decisions you’ll face is choosing between a recurve bow and a compound bow.
WhatsApp us
